Starter quiz
 Which of the following statements about the ammeter in the circuit shown is correct?
Which of the following statements about the ammeter in the circuit shown is correct?- The ammeter is measuring the current through the resistor.
- The ammeter is measuring the current through the lamp.
- The ammeter causes the lamp to go out. ✓
- The ammeter causes the lamp to light brightly.
-
 Which of the following statements about the ammeter in the circuit shown is correct?
Which of the following statements about the ammeter in the circuit shown is correct?- The ammeter is measuring the current through the cell, resistor and lamp.
- The ammeter is measuring the current through the resistor and the lamp.
- The ammeter should only have two connections. ✓
- The ammeter is measuring the current through the cell.
-
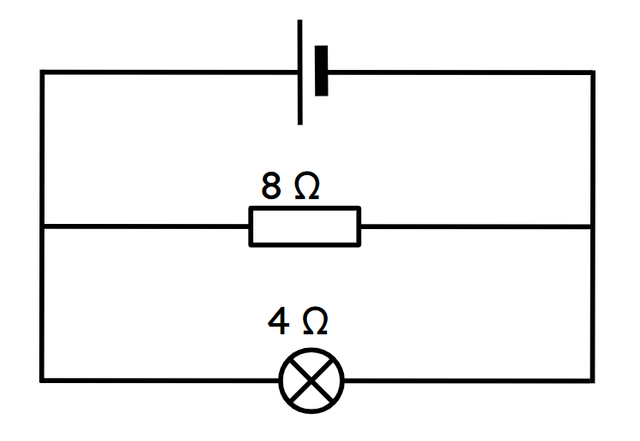 Which of the following statements about the current in the branches of a parallel circuit is correct?
Which of the following statements about the current in the branches of a parallel circuit is correct?- The current in the 8 branch is higher than in the 4 branch.
- The current in the 8 branch is lower than in the 4 branch. ✓
- The current in the 8 branch is the same as in the 4 branch.
-
- What will happen to the current through a parallel circuit branch if one 6 resistor in it is replaced with two 3 lamps in series?
- The current through the branch will remain the same. ✓
- The current through the branch will increase.
- The current through the branch will decrease.
-
 What will happen to the current through the cell in the following circuit if another lamp is added in parallel, as shown?
What will happen to the current through the cell in the following circuit if another lamp is added in parallel, as shown?- The current will increase. ✓
- The current will decrease.
- The current will remain the same.
-
- Which of the following changes occur if branches with components on them are added to a parallel circuit?
- It will increase the voltage only.
- It will increase the resistance only.
- It will increase the current only. ✓
- It will increase the voltage, resistance and current.
-
Exit quiz
- What will happen in a series circuit if a component (such as a resistor) is removed and the circuit is connected up again?
- The battery voltage will increase.
- The battery current will increase. ✓
- The total resistance will increase.
- The other components will have higher voltages across them. ✓
-
- The current pushed round a circuit with two 1.5 V cells connected in series is 0.4 A. What current will be pushed round if a third, identical cell is added in series?
- 0.2 A
- 0.4 A
- 0.6 A ✓
- 0.8 A
-
 What will happen to the other lamps in the circuit shown if lamp 2 'blows'?
What will happen to the other lamps in the circuit shown if lamp 2 'blows'?- All the other lamps will stay lit.
- All the other lamps will go off.
- Lamps 1 and 3 will go off but lamps 4 and 5 will stay lit. ✓
- Lamps 4 and 5 will go off but lamps 1 and 3 will stay lit.
-
 All of the lamps in the circuit shown are identical. What is the voltage across lamp 5?
All of the lamps in the circuit shown are identical. What is the voltage across lamp 5?- 2 V
- 3 V
- 4 V
- 6 V ✓
-
 All of the lamps in the circuit shown are identical. What is the voltage across lamp 2?
All of the lamps in the circuit shown are identical. What is the voltage across lamp 2?- 2 V
- 3 V
- 4 V ✓
- 6 V
-
- Which of the following changes occur as more resistors are added to a series circuit?
- The voltage across all components will increase.
- The current through all components will decrease. ✓
- The battery current will increase.
- The resistance of the whole circuit will increase. ✓
-
Worksheet
Loading worksheet ...
Presentation
Loading presentation ...
Video
Lesson Details
Key learning points
- With the same battery, two bulbs in parallel are brighter than two in series.
- With the same battery, current through two bulbs in parallel is bigger than through two in series.
- With the same battery, voltage across one of two bulbs in parallel is bigger than across one of two bulbs in series.
- With the same battery, two bulbs in parallel are transferring energy from the battery more quickly than two in series.
- A battery lighting two bulbs in parallel will run out faster than the same battery lighting the two bulbs in series.
Common misconception
The battery produces a fixed sized current that splits between each branch of a parallel circuit.
Consider each branch of a parallel circuit as a separate series circuit connected to an identical battery, in which the total current through the battery is determined by the current it can push through each of the branches added together.
Keywords
Series circuit - a circuit with a single loop
Current - the rate of flow of charge in a circuit
Voltage - a measure of the ‘push’ an electrical cell will give to charges
Parallel circuit - a circuit with junctions that lead to separate loops
+