Starter quiz
- Which of these is a force measurement?
- 30 kg
- 30 m
- 30 m/s
- 30 N ✓
- 30 J
-
 What feature of a distance-time graphs shows the speed?
What feature of a distance-time graphs shows the speed?- The horizontal axis.
- The verical axis.
- The gridlines.
- The gradient of the line. ✓
- The number of divisions on each axis.
-
- Which of these show how forces should be represented on diagram?
- Is drawn as an arrow. ✓
- Has a special colour for each type of force.
- Starts at the point where the force acts. ✓
- Points in the direction the force acts. ✓
- Must always have a pair drawn with it.
-
 Ben pushes a shopping trolley so it is moving quickly but then falls and lets go. Which of these forces still act on the trolley after he has let go?
Ben pushes a shopping trolley so it is moving quickly but then falls and lets go. Which of these forces still act on the trolley after he has let go?- Ben's push.
- A driving force keeping the trolley moving.
- A friction force due to the ground. ✓
- A normal contact force due to the ground. ✓
- A gravitational force due to Earth. ✓
-
 A student is measuring the average speed of a trolley between two points marked on a ramp. Which measurements do they need to make to find the speed?
A student is measuring the average speed of a trolley between two points marked on a ramp. Which measurements do they need to make to find the speed?- The mass of the trolley.
- The angle of the ramp.
- The time for the trolley to pass between the markers. ✓
- The time the trolley took to reach the markers.
- The distance between the two markers. ✓
-
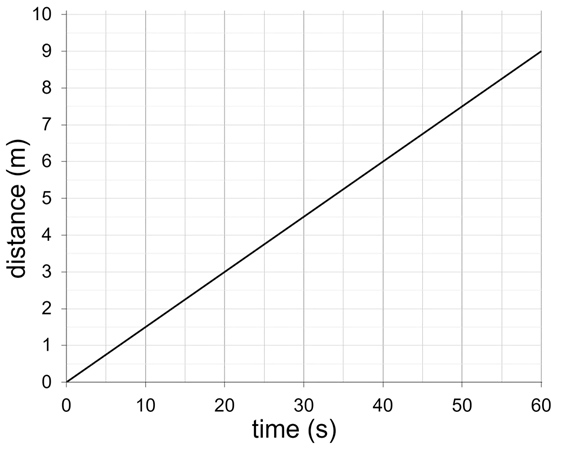 What is the average speed of this object?
What is the average speed of this object?- 0 m/s
- 0.15 m/s ✓
- 6.6 m/s
- 51 m/s
- 69 m/s
-
Exit quiz
 Match the key word with the description.
Match the key word with the description.- resultant force⇔The sum of forces on an object, accounting for direction. ✓
- gradient⇔The steepness of a line on a graph. ✓
- speed⇔Distance divided by time. ✓
- dynamics trolley⇔A wheeled device used in motion experiments. ✓
- acceleration⇔A change in speed. ✓
- Which of the following are acceleration?
- A change in the mass of an obejct.
- An increase in speed. ✓
- A decrease in speed. ✓
- Moving at constant speed in one direction.
- A change in distance.
-
 A person drags a box along the ground using a force of 25 N towards the right. A frictional force of 20 N acts on the box as it is dragged. What is the resultant force on the box?
A person drags a box along the ground using a force of 25 N towards the right. A frictional force of 20 N acts on the box as it is dragged. What is the resultant force on the box?- 45 N to the right
- 45 N to the left
- 5 N to the right ✓
- 5 N to the left
- 0 N
-
 A sprinter takes part in a 100 m race. Which statement describes how the forces change during the race?
A sprinter takes part in a 100 m race. Which statement describes how the forces change during the race?- The sprinter is at the same speed throughout the race as the force is constant.
- The sprinter's speed will only increase at the start of the race.
- The sprinter's speed will change as long as there is a resultant force acting. ✓
- The sprinter produces a forwards force only at the start of the race.
- The forces on the sprinter are always balanced so the speed stays constant.
-
 The figure shows a distance-time graph for a car. What does the graph show?
The figure shows a distance-time graph for a car. What does the graph show?- The speed of the car is increasing.
- The speed of the car is decreasing. ✓
- The forces on the car are balanced.
- There is a resultant force in the same direction as the car's movement.
- There is a resultant force in the opposite direction to the car's movement. ✓
-
- A firework rocket is launched vertically and it produces a large thrust for 5 s then the fuel runs out. Which answers correctly describe the rocket's motion?
- The rocket will accelerate upwards for the first 5 s. ✓
- The rocket will stop after 5 s.
- After 5 s the speed of the rocket will start to decrease. ✓
- After 5 s the rocket will start to move downwards.
- The rocket's speed will still be increasing after 5 s.
-
Worksheet
Loading worksheet ...
Presentation
Loading presentation ...
Video
Lesson Details
Key learning points
- A resultant force can change the speed of an object.
- The speed of an object changes throughout the time a resultant force is acting on it.
- The greater the gradient (steeper the line) on a distance-time graph, the faster the movement.
Common misconception
Pupils can think that change in speed is instantaneous due to forces, not over a period of time.
Demonstrate that objects continue to accelerate while the force is acting. Make the force easy to understand (e.g. a pulling string).
Keywords
Resultant force - The overall effect of a set of forces acting on an object.
Speed - A measurement of how fast something is moving, found from the distance travelled divided by the time taken.
Dynamics trolley - A small wheeled cart used in motion experiments.
Acceleration - A change in speed or direction of movement.
+