Starter quiz
 What does it mean to be identical to something?
What does it mean to be identical to something?- to be the complete opposite of it
- to be very different to it
- to share some similarities
- to be exactly the same ✓
-
- All living things can reproduce. What does this mean?
- They make more living things of the same type. ✓
- They live in habitats that they are suited to.
- They make their own food.
- They have a life cycle.
-
 What is the offspring of a living thing?
What is the offspring of a living thing?- the group they live and hunt with
- the food they gather from their habitat
- the young they create through reproduction ✓
-
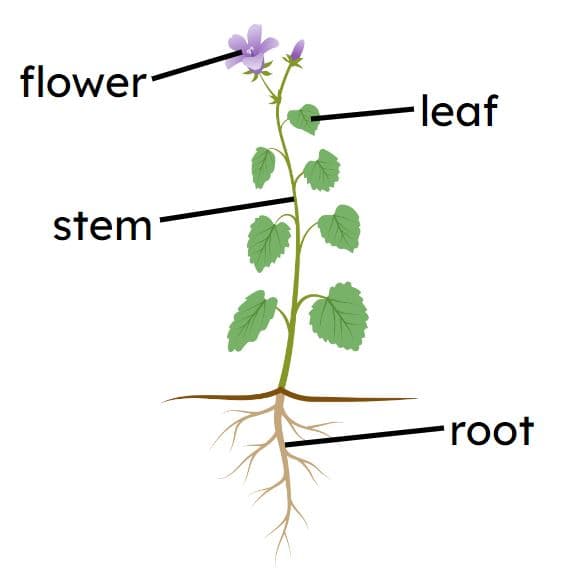 The ______ is the part of the plant that allows it to reproduce by making seeds.
The ______ is the part of the plant that allows it to reproduce by making seeds.- 'flower' ✓
- Before flowers can make seeds, they must be pollinated. What is pollination?
- when pollen is made by the male anthers of a flower
- when pollen is transferred from a male part of a flower to a female part ✓
- when animals eat pollen from the female part of the flower and make honey
-
- Starting with the one that happens first, put the steps of flowering plant reproduction into the correct order.
- 1⇔A flower is pollinated by animals or the wind.
- 2⇔The flower is fertilised when pollen moves to its ovary.
- 3⇔Seeds are formed inside the ovary.
- 4⇔Seeds are dispersed.
Exit quiz
 Which statement is correct?
Which statement is correct?- Plants can only reproduce by pollination and fertilisation.
- Plants cannot reproduce without help from animals.
- Plants can reproduce in different ways. ✓
-
- What is asexual reproduction in plants?
- Reproduction that produces only one offspring.
- Reproduction that creates many offspring.
- Reproduction by a single plant. ✓
- Reproduction that involves two parent plants.
-
- Which of these is not an example of asexual reproduction in plants?
- seeds ✓
- bulbs
- runners
- tubers
-
 Offspring that are produced asexually from a single parent plant are called ______, which means they are identical to their parent plant.
Offspring that are produced asexually from a single parent plant are called ______, which means they are identical to their parent plant.- 'clones' ✓
 Some plants can reproduce asexually using tubers or bulbs. Whereabouts on plants are tubers and bulbs found?
Some plants can reproduce asexually using tubers or bulbs. Whereabouts on plants are tubers and bulbs found?- in the centre of flowers
- at the top of the stem
- on edge of the leaves
- under the ground beneath the plant ✓
-
- Some plants can reproduce asexually using runners. What does this mean?
- Growing special food stores under the ground that can grow their own new plants.
- Growing long, horizontal stems that can take root and grow new plants. ✓
- Forming seeds inside an ovary following fertilisation.
-
Worksheet
Presentation
Video
Lesson Details
Key learning points
- Plants reproduce to make new plants, or offspring, in different ways.
- Plants can reproduce asexually, which means a single parent plant can reproduce on its own.
- Plants produced asexually are identical to their parent plant; they are clones.
- Bulbs, runners and tubers are examples of asexual plant reproduction.
Common misconception
Pupils may think that the only way for plants to reproduce is by making seeds (i.e. as a result of sexual reproduction).
Plants can reproduce asexually in a number of ways. Use the lesson resources to show alternative ways for plants to reproduce that don’t involve pollination, fertilisation and seed formation.
Keywords
Reproduce - When living things reproduce they create offspring.
Offspring - Living things create offspring when they reproduce.
Parent plant - A parent plant is a plant that has reproduced and created offspring.
Asexual - Asexual reproduction involves one parent and produces offspring that has the same characteristics as the parent.
Clone - Clones are offspring that have been created asexually and have identical characteristics to their parent.