Starter quiz
- What happens when free electrons in a metal collide with metal ions?
- the metal ions vibrate less vigorously
- the metal ions vibrate as before
- the metal ions vibrate more vigorously ✓
-
- What causes free electrons in a metal to move?
- a resistance
- a current
- a p.d. ✓
-
- Which of the following effects will result from a higher p.d. across a metal wire in a working electrical circuit?
- its free electrons will move faster ✓
- a higher current will flow through it ✓
- the metal will become cooler
- the metal ions will vibrate less vigorously
-
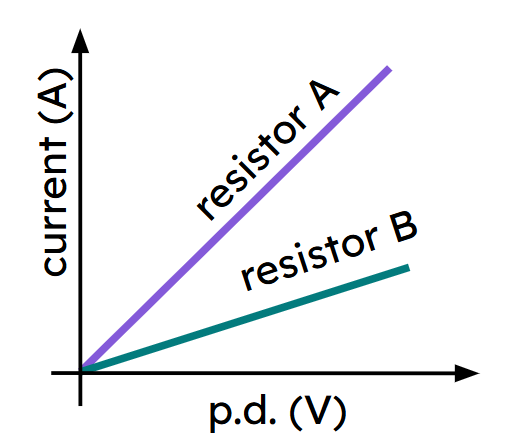 Which of the followings statements about resistors A and B is correct?
Which of the followings statements about resistors A and B is correct?- resistor A has a higher resistance than resistor B
- resistor A has a lower resistance than resistor B ✓
- both resistors have the same resistance
- it is not possible to say which resistor has the higher resistance
-
- Which of the following elements is a semiconductor?
- iron
- copper
- aluminium
- silicon ✓
-
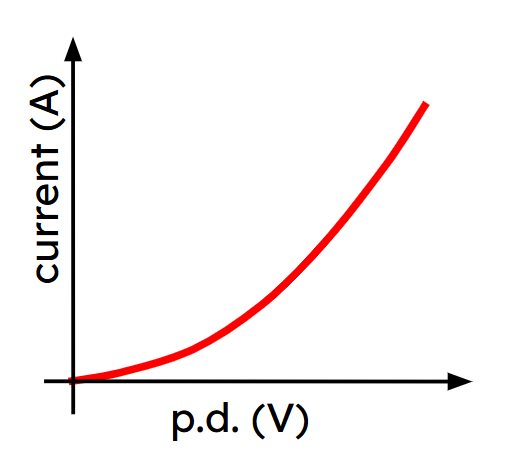 Which of the following statements about the I–V graph shown is correct?
Which of the following statements about the I–V graph shown is correct?- as the p.d. increases, the resistance increases
- as the p.d. increases, the resistance decreases ✓
- the resistance remains the same as the p.d. changes
- it is not possible to say if the resistance changes
-
Exit quiz
 Which of the following components are shown in the image?
Which of the following components are shown in the image?- resistors
- capacitors
- thermistors
- diodes ✓
-
- Which of the following statements about the ends of a diode is correct?
- there are two positive ends
- there are two negative ends
- there is one positive and one negative end ✓
- both ends are neutral
-
- Which of the following are the main chemical elements that can be used to make diodes?
- copper
- aluminium
- silicon ✓
- germanium ✓
-
- What type of voltmeter is needed to measure the potential difference (p.d.) across a diode: one that measures in volts (V), millivolts (mV), or kilovolts (kV)?
- one that measures in millivolts (mV) ✓
- one that measures in volts (V)
- one that measures in kilovolts (kV)
-
- When the positive end of a diode is connected to the positive terminal of a battery and the negative end of the diode is connected to the negative terminal of the battery, the diode is ...
- in forward bias. ✓
- in reverse bias.
- at the threshold p.d.
- overloaded.
-
- Which of the following occurs when the p.d. across a forward–biased diode is increased to just above the threshold p.d.?
- the current increases ✓
- the resistance increases
- the current stops flowing
-
Worksheet
Loading worksheet ...
Presentation
Loading presentation ...
Video
Lesson Details
Key learning points
- The properties of a diode are different, depending on the direction of p.d. across it.
- An appropriate range of p.d. includes 0 V and the maximum voltage of the diode and at least four other readings.
- An appropriate range for a diode includes the maximum p.d. in both directions, with positive and negative values.
- For electricity investigations, it is good practice to take many more than the minimum number of measurements.
Common misconception
The gradient of an I–V graph is equal to 1/R because I = V ÷ R.
Explain how the equation for a straight line graph y = mx + c does not apply in this case because the graph is not a straight line.
Keywords
Diode - an electrical component that is used to prevent current flow in one direction
Semiconductor - a material that has both metallic and non-metallic properties
Threshold p.d. - the potential difference at which a diode allows current to flow
Reverse–biased - when a diode is reverse–biased, it prevents current from flowing
Forward–biased - when a diode is forward–biased, it allows current to flow
+