Starter quiz
- Which of the following are equivalent to ?
- ✓
- ✓
- ✓
-
-
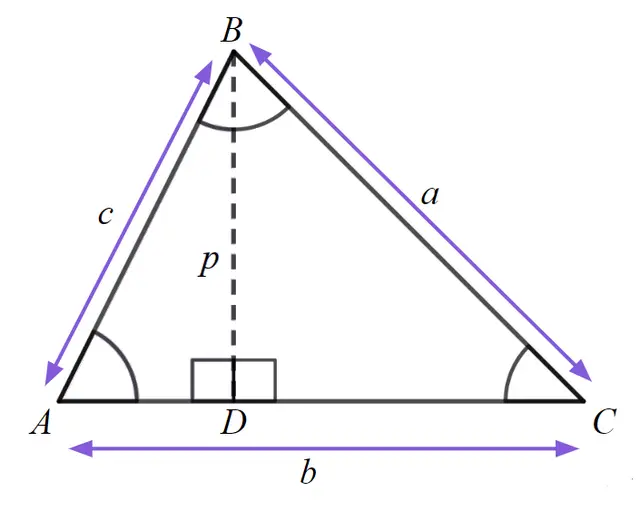 Using , identify all the rearrangements.
Using , identify all the rearrangements.- ✓
- ✓
-
-
-
 Using , identify all the rearrangements.
Using , identify all the rearrangements.-
- ✓
- ✓
-
-
- An isosceles triangle has lengths 10 cm, 10 cm and 16 cm. The area of the isosceles triangle is ______cm.
- '48' ✓
- An equilateral triangle has lengths of 10 cm. The area of the triangle, to 1 decimal place, is ______cm.
- '43.3' ✓
- A regular hexagon has lengths of 6 cm. The area of the hexagon, to the nearest integer, is ______cm.
- '94' ✓
Exit quiz
- When do we use the sine sule?
- For calculating either an unknown side length or the size of an unknown angle ✓
- For calculating the area of a triangle
- For calculating the area of a circle
- For ensuring we write signs properly
-
 Identify the correct ways to express using the diagram.
Identify the correct ways to express using the diagram.- ✓
- ✓
-
-
-
- Which of the following are correct versions of the sine rule?
- ✓
- ✓
- ✓
- ✓
-
-
 Length is opposite angle A. Work out the size of length giving your answer to 2 decimal places.
Length is opposite angle A. Work out the size of length giving your answer to 2 decimal places.- '9.74 cm' ✓
 Length is opposite angle B. Work out the size of length giving your answer to 2 decimal places.
Length is opposite angle B. Work out the size of length giving your answer to 2 decimal places.- '13.1 cm' ✓
 Work out the size of angle giving your answer to 1 decimal place.
Work out the size of angle giving your answer to 1 decimal place.- '57.0' ✓
Worksheet
Loading worksheet ...
Presentation
Loading presentation ...
Video
Lesson Details
Key learning points
- The sides of a triangle are proportional to the sines of their opposite angles
- A diagram can aid with understanding this
- The sine rule is useful when you know an angle and side pair and wish to find another pair
- In order to do this, you will need either a side length or an angle
Common misconception
Pupils may be uncertain about which angle pairs with which side.
The angle is paired with the side length that is opposite.
Keywords
Sine rule - The sine rule is a formula used for calculating either an unknown side length or the size of an unknown angle.
+